Introduction
The default routing algorithm for how the ASP.NET MVC framework invokes actions is like {controller}/ {action}/ {id} patterns.
But this becomes more complex when you have two methods with the same name, or when you invoke an action when form data is submitted, or execute a method only when an AJAX request is made.
Implementation
 This can be done using
This can be done using ActionMethodSelector attributes. We generally use method selectors like:
AcceptVerbsActionName
ActionMethodSelector attributes. We generally use method selectors like:AcceptVerbsActionNameAcceptVerbs
This attribute is used when we want to execute some action when a particular HTTP operation is performed like POST, GET, DELETE, etc. E.g.:
Hide Copy Code
[AcceptVerbs(HttpVerbs.Post)]
public ActionResult Create(Employee employee)
{
// To Do Code Here
}
The above method is executed when an HTTP POST operation is performed.
AcceptName
This attribute is used when you expose an action name with a different name than its method name, or you can use an action name attribute to expose two methods with the same name as the action with different names. E.g.:
Hide Copy Code
[ActionName(“Edit”)]
[AcceptVerbs(HttpVerbs.Get)]
public ActionResult Edit_GET(Employee employee)
{
// To Do Code Here
}
[ActionName(“Edit”)]
[AcceptVerbs(HttpVerbs.Post)]
Public ActionResult Edit_POST(Employee employee)
{
// To Do Code Here
}
Custom Action Method Selector
You can build your own ActionMethodSelector attributes by deriving from the abstractActionMethodSelectorAttribute class.
This is an extremely simple class; you just need to override the method named IsValidForRequest (). If this returns false, this action method is not executed.
Now take a simple example of the Custom Action Method Selector. Develop an Ajaxmethod custom attribute useful for when you want to execute some action when an AJAX request is made.
The first step is to create an MVC application. Then add a class file named AjaxMethod.cs and inherit that class from ActionMethodSelectorAttribute. Then override a method named IsValidForRequest(). Your class will look like below:
Hide Copy Code
public class AjaxMethod:ActionMethodSelectorAttribute
{
public override bool IsValidForRequest(ControllerContext controllerContext,
System.Reflection.MethodInfo methodInfo)
{
return controllerContext.HttpContext.Request.IsAjaxRequest();
}
}
In the IsValidForReuest method, we check the Request object for the AJAX request.
Now we can use the Ajaxmethod attribute in our controller when you want to execute some action only when an AJAX request comes. For this, add a controller named NewsController into the controller folder. In this controller, we define two index actions: first index action only executes when a page is posted back and the second action is invoked when an AJAX request comes. Your controller will look like below:
Hide Shrink  Copy Code
Copy Code
public class NewsController : Controller
{
private readonly List<string> _news = new List<string>();
private Random _rnd = new Random();
public NewsController()
{
_news.Add("Moon Explodes");
_news.Add("Stock Market up 200 percent");
_news.Add("Talking Robort Created!");
}
//
// GET: /News/
public ActionResult Index()
{
var SelectedIndex = _rnd.Next(_news.Count);
ViewData["News"] = _news[SelectedIndex];
return View();
}
[AjaxMethod]
[ActionName("Index")]
public string Index_AJAX()
{
var SelectedIndex = _rnd.Next(_news.Count);
return _news[SelectedIndex];
}
}
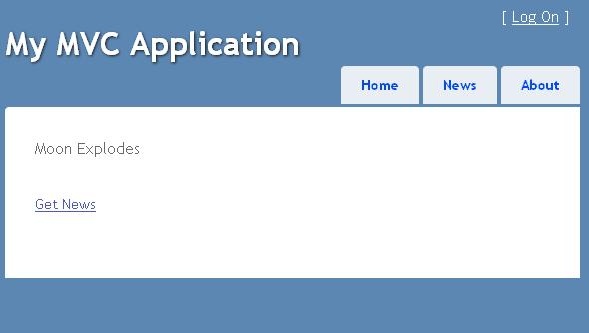
Now add a View named index.aspx for displaying news and add the below markup into that:
Hide Copy Code
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../Scripts/MicrosoftAjax.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../Scripts/MicrosoftMvcAjax.js"></script>
<%= Ajax.ActionLink("Get News", "Index", new AjaxOptions { UpdateTargetId = "news" })%>
<span id="news"%><%:ViewData["News"] %></span>
Now run the application. You will find that when the page loads the first time the first index action executes and when you click on the GetNews link at that time, the second index action executes. The first time, it will go check the Ajaxmethod attribute but the IsValidForRequest method will return false and then it will execute the first index action, but when you click on the link at that time, IsValidForRequest returns true and executes the second action.
ActionMethodSelector attributes by deriving from the abstractActionMethodSelectorAttribute class.IsValidForRequest (). If this returns false, this action method is not executed.Ajaxmethod custom attribute useful for when you want to execute some action when an AJAX request is made.ActionMethodSelectorAttribute. Then override a method named IsValidForRequest(). Your class will look like below:IsValidForReuest method, we check the Request object for the AJAX request.Ajaxmethod attribute in our controller when you want to execute some action only when an AJAX request comes. For this, add a controller named NewsController into the controller folder. In this controller, we define two index actions: first index action only executes when a page is posted back and the second action is invoked when an AJAX request comes. Your controller will look like below: Copy Code
Copy CodeAjaxmethod attribute but the IsValidForRequest method will return false and then it will execute the first index action, but when you click on the link at that time, IsValidForRequest returns true and executes the second action.Conclusion
Some of the least customized but very useful extension points in ASP.NET MVC are action method selector attributes. But using them, we can make seemingly complex things trivial.
Action Selectors:
Action selectors help routing engine to select correct action method to execute for a particular request. Action selectors are attributes that can be applied to action methods. MVC 5 includes following action selector attributes:
- ActionName
- NonAction
- ActionVerbs
Action selectors help routing engine to select correct action method to execute for a particular request. Action selectors are attributes that can be applied to action methods. MVC 5 includes following action selector attributes:
- ActionName
- NonAction
- ActionVerbs
ActionName:
ActionName attribute allow us to specify different action name than method name. Consider following example.
In the above example, we have applied ActioName("find") attribute to GetById action method. So now, action name is find instead of GetById. This action method will be invoked on http://localhost/student/find/1 request instead of http://localhost/student/getbyid/1request.
ActionName attribute allow us to specify different action name than method name. Consider following example.
In the above example, we have applied
ActioName("find") attribute to GetById action method. So now, action name is find instead of GetById. This action method will be invoked on http://localhost/student/find/1 request instead of http://localhost/student/getbyid/1request.NonAction:
NonAction selector attribute indicates that a public method of a Controller is not an action method. Use NonAction attribute when you want public method in a controller but do not want to treat it as an action method.
For example, following GetStudent public method cannot be invoked like action method.

NonAction selector attribute indicates that a public method of a Controller is not an action method. Use NonAction attribute when you want public method in a controller but do not want to treat it as an action method.
For example, following GetStudent public method cannot be invoked like action method.

Points to Remember :
- MVC framework routing engine uses Action Selectors attributes to determine which action method to invoke.
- Three action selectors attributes are available in MVC 5
- ActionName
- NonAction
- ActionVerbs
- ActionName attribute is used to specify different name of action than method name.
- NonAction attribute marks the public method of controller class as non-action method. It cannot be invoked.
- MVC framework routing engine uses Action Selectors attributes to determine which action method to invoke.
- Three action selectors attributes are available in MVC 5
- ActionName
- NonAction
- ActionVerbs - ActionName attribute is used to specify different name of action than method name.
- NonAction attribute marks the public method of controller class as non-action method. It cannot be invoked.
No comments:
Post a Comment